Design is a funny word. Some people think design means how it looks. But, of course, if you dig deeper, it’s really how it works. To design something really well, you have to ‘get it’. You have to really grok [understand] what it’s all about. – Steve Jobs
UX design is User Experience design. It’s all the behind the scenes work that goes into creating an app, site, software, service including –
- User research
- Design research
- Information architecture
- Industrial design
- Interaction design
- Experience design
- UI design
- Content strategy
- Rapid prototyping
- Rapid iteration
- Usability testing
- And more
Design is concerned with how things work, how they are controlled and the nature of the interaction between people and technology. Make technology easy to use. User experience (UX) designers make technology easier and more enjoyable to use. They create products and interfaces that are useful, usable, accessible to users.
Focus on understanding the habits, behaviors, motivations, emotions of the users. Understand deeply the problem and who you’re designing for. This helps you prototype and iterate on solutions. You’re not practicing UX design unless you’re talking to actual users! Talk early, talk often. The later in the process that a mistake is detected, the more expensive it is to fix.

- Industrial design is the professional service of creating and developing concepts and specifications that optimize the function, value and appearance of products and systems for the mutual benefit of both user and manufacturer (Source: Industrial Design Society of America’s site)
- Interaction design focuses on how people interact with technology. The goal is to enhance people’s understanding of what can be done, what is happening, what has just occurred. Interaction design draws upon the principles of psychology, design, art and emotion to ensure a positive, enjoyable experience.
- Experience design is the practice of designing products, processes, services, events and environments with a focus placed on the quality and enjoyment of the total experience.
UI design stands for User Interface design, which is the visual or graphical side of design. Some UX designers will also do some UI (UI & UX), but other UX designers will only go as far as research and wireframes. What’s the difference between UI and UX design ? UI design is an integral part of UX design.
User Centered Design
Design thinking is a powerful process of problem identification and solving that begins with understanding unmet customer needs. From that insight emerges a process for innovation that encompasses concept development, applied creativity, prototyping, experimentation. When design thinking approach is applied to business, the success rate for innovation improves substantially.
User Centered Design (UCD) is a development methodology
Use this methodology to create innovative solutions working collaboratively with your users. User understanding is about researching and identifying your primary users, meeting with them, observing them to understand their requirements (stated and unstated), goals, challenges and constraints. This is an important step that differentiates UCD from traditional waterfall development methodology.
UCD is interdisciplinary
This includes end users, program managers, developers, testers and business stakeholders. Validate your design by developing prototypes, get early feedback from the users and improve the design based on the feedback.
UCD is an iterative process
You design, test, fail, try again. It’s about building the optimal solution, not just building it optimal. Come up with creative solutions that your users will embrace. Create, inspire, support compelling and effective experiences through deep research driven user understanding and innovative design, best practices and continuous improvement in quality in use.
UCD empowers innovation
Typically, startups to enterprises spend all resources in development. However, they learn later that customers do not need some features. This spend could have been better focused on leveraging UCD principles. Companies spend enormous amount in marketing, but very little in understanding their users, what’s working and what’s not working for them. UCD empowers creativity and innovation through rapid iteration. Add a drop of UCD and see for yourself. The heart of UCD occurs during requirements and design.

Design Innovation Process
UCD arrives at solutions that are viable, feasible, desirable
Business Model
“What’s viable?” Goals and requirements defined by the business which sets the foundation for the design of the application
Technology
“What’s feasible?” Proposed technologies (Web, mobile, SharePoint, etc.) considered for development of the application
User Experience
“What’s desirable?” Overall experience and satisfaction that a user has when using the application

UCD and Usability
UCD is a development process you use to develop innovative solutions that help your users accomplish their tasks quickly and easily.
Usability is a quality indicator of the output delivered by the UCD process. It refers to the degree to which solutions are easy to use, efficient, satisfying to users.
When it comes to usability, users say Don’t Make Me Think.
Don’t Make Me Think – Steve Krug
A classic. This book is your go-to source for anything on usability. Usability is a big part of UX, making this a great book to help you as a UX professional. Steve Krug states that good design is design where you do not have to think about how you should interact with the design. Good design makes it easy for you to complete your tasks.

Revisiting 7 principles from Steve Krug’s common sense approach to Web and mobile usability –
- Your goal should be for each page or screen to be self-evident, so that just by looking at it the average user can say ‘I get it’
- Graphical user interfaces have long been built on principles of shifting focus – picking up a tool, opening and closing a window, etc. – but they still leave us staring at a cluttered screen. If something requires a large investment of time—or looks like it will—it’s less likely to be used.
- Get rid of half of the words on each page, then get rid of half of what’s left. Make it simple. Make it memorable. Make it inviting to look at. Make it fun to read.
- As a user, I should never have to devote a millisecond of thought to whether things are clickable — or not
- The main thing you need to know about instructions is that no one is going to read them
- Occasionally, time spent reinventing the wheel results in a revolutionary new rolling device. But usually it just amounts to time spent reinventing the wheel.
- The only way to find out if it really works is to test it
Other factors to keep in mind with respect to usability –
- The aesthetic-usability effect refers to users’ tendency to perceive attractive products as more usable. People tend to believe that things that look better will work better. Apple’s success is an excellent example of the competitive advantage of paying attention to aesthetics.
- A mental model is what the user believes about the system at hand. This model is based on belief, not facts. Individual users each have their own mental model. Understanding the concept of mental models can help you make sense of usability problems in your design. When you see people make mistakes on your site, the reason is often because they’ve formed an erroneous mental model.
- Consider adding a signature element. The signature element of iPod’s design and user interface is the scroll wheel. Yet, for usability and cost reasons, it has gone through four distinct generations in the short life of the product. What is interesting is that the industrial design (ID) team, led by Jonathan Ive, has been able to accomplish this, and still preserve the essence of design language.
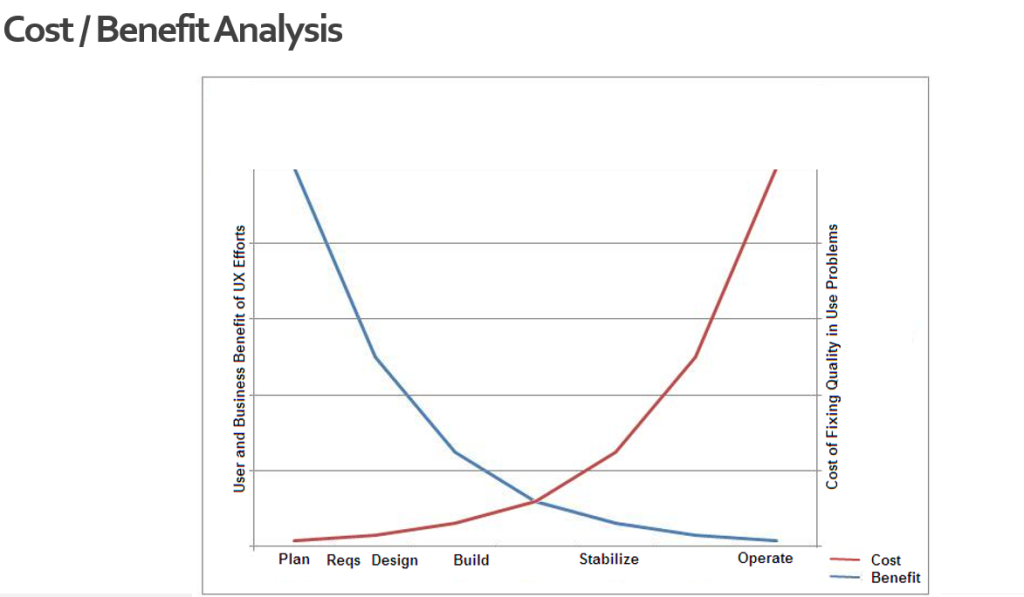
1:10:100 ratio
The cost of fixing usability issues reduces by leveraging UCD methodology. This is achieved by validating design prototypes early in the cycle and improving the design based on feedback.
Usability aware organizations follow the rule of thumb that once in development, it costs roughly 10 times as much as fixing the same problem in design. Once the system is released, it costs 100 times as much as fixing it in design. (Source: Book Cost Justifying Usability)
Business value of investing in great user experience
There’s tremendous business value in enabling great user experience. Industry research shows >30% improvement in productivity, usage, satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
Categories of Benefit
- Improved Business Effectiveness
- Faster realized ROI- productivity
- Improved NSAT/CPE and Loyalty
- Stronger brand association
Cost reduction
- For training and support
- For development cost through design reuse
- Reduction in rework and post-production fixes
Increased Customer, Partner and Employee Experience
- Improved ease of experience integration
- Focus on enhancements and new products
What has most value
Computer shouldn’t be unusable. You don’t need to know how to work a telephone switch to make a phone call, or how to use Hoover Dam to take a shower, or how to work a nuclear-power plant to turn on the lights.
Usability is a big part of UX. Good design is design where you do not have to think about how you should interact with the design. Good design makes it easy for you to complete your tasks.
Read more about what you stand to lose in the absence of good design.
Read more about how design enabled Apple’s turnaround story in 1997.
How do you engage with your users ?
How do you measure if the products and services meet your users’ stated and unstated needs ?
Do share in the comments!
Like this article ? How about giving it a like and share ? Thank you!
